
HOW TO CONTROL YOUR DIABETES
Diabetes, a disease condition characterised by elevated blood sugar levels, poses a significant health challenge worldwide. It impacts millions of individuals, necessitating careful management to prevent complications and enhance overall well-being. , Here we will explore various strategies for effectively controlling diabetes, encompassing dietary habits, physical activity, blood sugar monitoring, medication management, stress reduction, and preventive measures.
Understanding Diabetes: Diabetes has different forms, including Type 1, 2, and gestational diabetes. While the origins of each type may vary, they share the common feature of impaired blood sugar regulation. Insulin is a primary hormone the pancreas produces and plays a crucial role in this process. In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas makes little to no insulin; in Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin’s effects. Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that mainly develops during pregnancy and the lactation period, posing risks to both the mother and the baby.
Healthy Eating Habits: A balanced diet habit is important to managing diabetes effectively. Emphasise consuming nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control and carbohydrate monitoring are essential for stabilising blood sugar levels. Avoiding sugary beverages, processed foods, and excessive carbohydrate intake is imperative. Instead, opt for high-fiber foods that promote satiety and aid in blood sugar regulation. Consistency in meal timing and regularity is equally important in maintaining stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Physical activity: physical activity is not just beneficial; it is a cornerstone of diabetes management. Regular exercise offers numerous advantages, including improved insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and weight management. Please aim to engage in at least 150 to 200 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, supplemented with strength training exercises two to three times weekly. Choose activities you enjoy, whether walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing, as this enhances adherence to exercise routines and promotes long-term health.
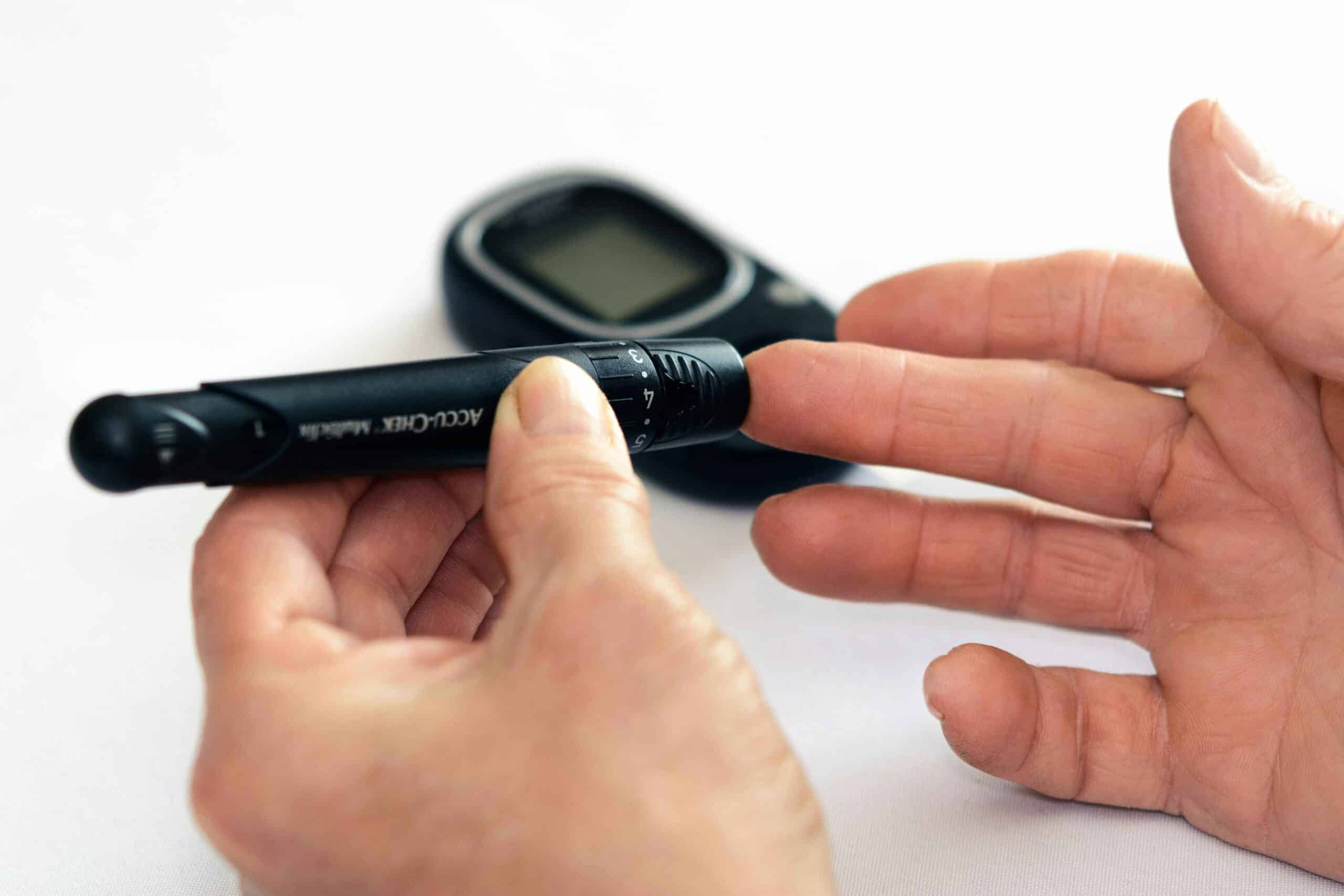
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regular monitoring of your blood glucose levels is crucial for individual diabetes patients. This allows for tracking blood sugar responses to food, exercise, medication, and other factors—Utilise glucometers to measure blood sugar levels at home and maintain records to identify patterns over time. Remember, collaboration with healthcare providers is critical to establishing target ranges for blood sugar levels and adjusting treatment plans based on the findings, providing you with the support and reassurance you need.
Medication and Treatment: Many individuals with diabetes require medication to manage their condition effectively. Common medications include insulin, oral medications, and other injectable drugs. Adherence to prescribed treatment regimens is essential, as is regular communication with healthcare providers regarding any concerns or changes in condition. Awareness of potential side effects of medications ensures timely intervention and optimised treatment outcomes.
Stress Management and Emotional or Mental Well-being: Managing stress and maintaining emotional well-being is vital for diabetes care. Stress significantly affect blood sugar levels and overall health. Thus, it’s essential to embrace stress management strategies like relaxation exercises, deep breathing, meditation, and seeking support from loved ones, close relatives or mental health experts. Prioritising emotional well-being involves addressing feelings of anxiety, depression, or burnout promptly to ensure comprehensive diabetes management.
Preventive Measures: Taking proactive steps is crucial in minimising diabetes-related complications. These include maintaining a healthy body weight, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, smoking, and attending regular medical check-ups and screenings. By being proactive and collaborating with healthcare providers, you manage your diabetes care, ensuring early intervention and optimal health outcomes.
In conclusion: How To Control Your Diabetes
this comprehensive guide empowers individuals with diabetes, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to take control of their health. By incorporating strategies such as healthy eating habits, regular exercise, blood sugar monitoring, medication management, stress reduction, and preventive measures, individuals can effectively control their diabetes and improve their overall well-being. This knowledge and these resources are vital to reducing the burden of diabetes and enhancing quality of life.
Leave a Reply