Introduction
Microbiology, is the study of microscopic organisms and their interactions with the environment has a rich history filled with breakthroughs and discoveries that have revolutionized our understanding of the world around us. In this article, we will delve into the journey of microbiology, from its humble beginnings to its modern-day significance.
The Early Pioneers of Microbiology
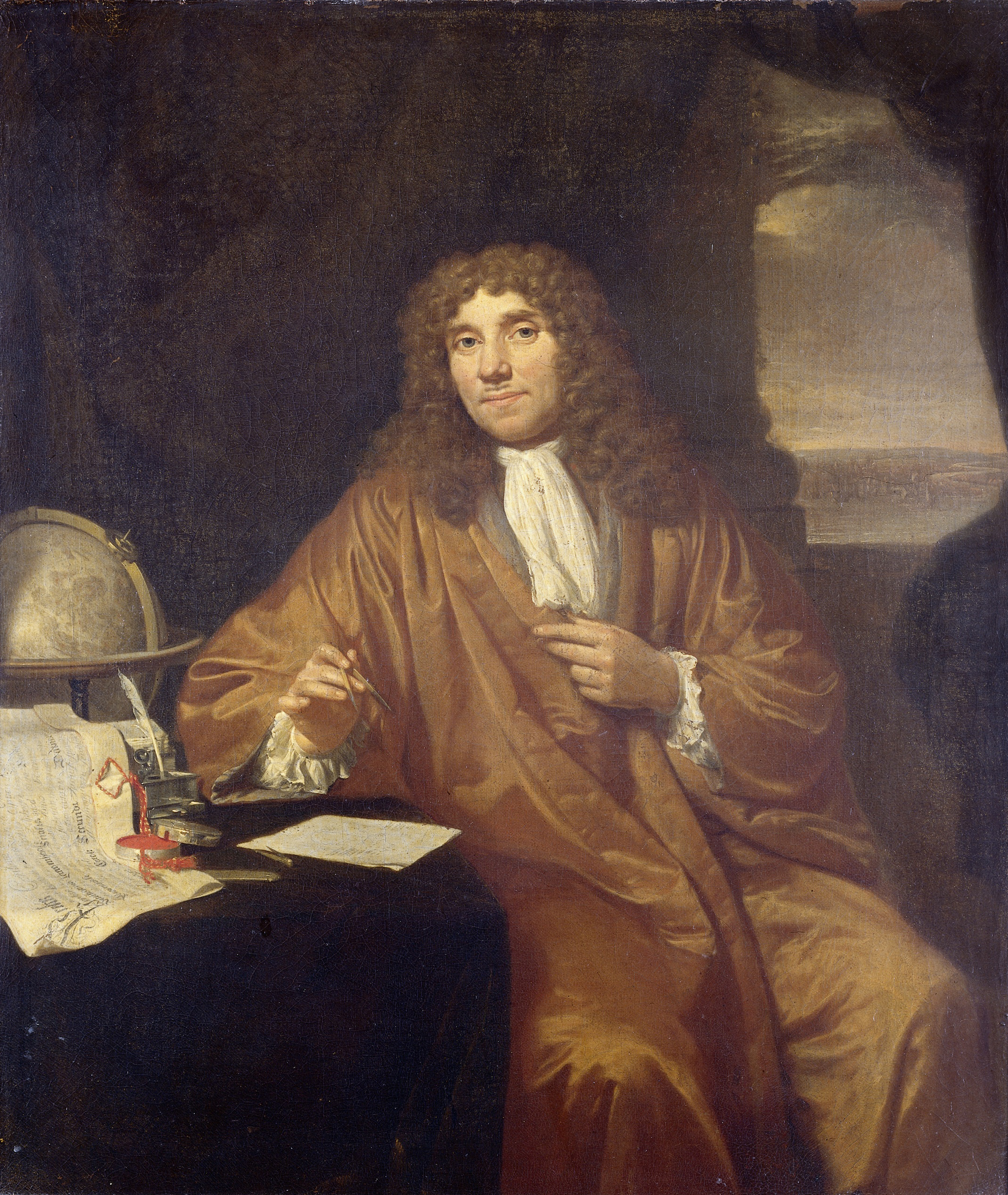
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek: The Father of Microbiology
- In the 17th century, Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek crafted the first microscope and made groundbreaking observations of microscopic organisms, earning him the title of the “Father of Microbiology.”
- Leeuwenhoek’s meticulous observations of bacteria, protozoa, and other microorganisms laid the groundwork for microbiology.

Louis Pasteur and Germ Theory
- French scientist Louis Pasteur ushered in the era of modern microbiology with his experiments on fermentation and pasteurization.
- Pasteur’s development of the germ theory of disease revolutionized medicine by establishing the link between microorganisms and infectious diseases.

The Golden Age of Microbiology
Robert Koch and the Birth of Medical Microbiology
- German physician Robert Koch made significant contributions to medical microbiology by identifying the causative agents of anthrax, tuberculosis, and cholera.
- Koch’s postulates provided a systematic approach for linking a specific microorganism to a particular disease, shaping the field of epidemiology.
Alexander Fleming and the Discovery of Penicillin
- Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming’s serendipitous discovery of the penicillin in the year of 1928 marked a turning point in the treatment of bacterial infections.
- The development of antibiotics revolutionized medicine and remains a cornerstone of modern healthcare practices.
Modern Advancements in Microbiology
Genomics and Microbial Diversity
- The advent of genomics has enabled researchers to study the genetic makeup of microorganisms, shedding light on their diversity and ecological roles.
- Metagenomics, the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples, has unveiled a vast array of microbial life previously unknown to science.
Microbiome Research and Human Health
- The human microbiome, the collection of microorganisms living in and on the human body, has emerged as a key area of research in microbiology.
- Studies on the microbiome’s impact on human health, immunity, and disease have opened up new therapeutic avenues and personalized medicine approaches.
Conclusion
The history of microbiology is proof of the interest, tenacity, and inventiveness of people in solving the puzzles surrounding the microbial world. Microbiology has influenced our understanding of life at the microscopic level ever since its discovery by Leeuwenhoek and Pasteur and continues to do so with the latest developments in genomes and microbiome research. Let us proceed with curiosity and wonder as we continue to investigate the complex and amazing field of microbiology.
Leave a Reply