Diabetes can affect almost every part of your body — including your eyes. One of the most common and serious complications is diabetic retinopathy, a condition that damages the tiny blood vessels in your retina, leading to vision problems and even blindness if left untreated.
Understanding retinopathy treatment in diabetes is essential for early prevention and effective management. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy — from its causes and symptoms to diagnosis and the latest treatment options available.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
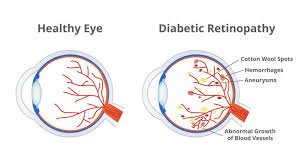
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye disease that affects people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage the delicate blood vessels in the retina — the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
Over time, this damage can cause these vessels to swell, leak, or close off completely, reducing oxygen supply to the retina. In severe cases, new but fragile blood vessels may grow, leading to bleeding and scarring.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy:
Tiny bulges (microaneurysms) form in the retinal blood vessels. Vision is often still normal. - Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy:
Blood vessels that nourish the retina become blocked. Vision may begin to blur. - Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy:
More blood vessels become blocked, cutting off oxygen supply and triggering new vessel growth. - Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR):
The most advanced stage where new, fragile vessels grow and may leak blood into the eye, leading to vision loss or blindness.
Common Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
In early stages, there may be no symptoms at all, which is why regular eye check-ups are so important. As the disease progresses, symptoms can include:
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Spots or strings (floaters) in your vision
- Sudden vision loss
If you experience any of these signs, you should see an ophthalmologist immediately.
Causes and Risk Factors
The main cause of diabetic retinopathy is high blood sugar. However, other factors can increase your risk:
- Duration of diabetes – The longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk.
- Poor blood sugar control
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Pregnancy (in women with diabetes)
Managing these risk factors is crucial for protecting your eyesight.
How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive dilated eye exam by an eye specialist. Key diagnostic methods include:
- Visual acuity test: Measures how well you see at various distances.
- Dilated eye exam: Allows your doctor to see blood vessels and the back of your eye.
- Fluorescein angiography: A dye is injected into your arm to highlight blood vessel leaks.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): A non-invasive scan that shows detailed images of your retina.
Early diagnosis can prevent or delay vision loss in most cases.
Retinopathy Treatment in Diabetes
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of the disease. The goal is to slow or stop the progression and prevent vision loss.
1. Controlling Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure
The first and most important step in treating diabetic retinopathy is maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. You can achieve this through:
- A balanced diabetic diet
- Regular exercise
- Medication or insulin therapy
- Regular monitoring of glucose levels
Keeping blood pressure and cholesterol in check is also essential to reduce further eye damage.
2. Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation)
This is one of the most common treatments for diabetic retinopathy. Laser surgery helps seal leaking blood vessels and shrink abnormal ones.
There are two main types:
- Focal laser treatment: Targets specific leaking vessels.
- Scatter laser treatment (panretinal photocoagulation): Treats a wider area to shrink abnormal vessels.
Laser treatment is effective in preventing vision loss, especially when detected early.
3. Anti-VEGF Injections
These injections target a protein called VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), which promotes abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina.
Common anti-VEGF medications include:
- Ranibizumab (Lucentis)
- Aflibercept (Eylea)
- Bevacizumab (Avastin)
These drugs are injected directly into the eye, helping to reduce swelling and improve vision. Regular sessions may be required depending on the patient’s response.
4. Vitrectomy Surgery
In advanced stages, especially in proliferative diabetic retinopathy, vitrectomy may be necessary.
This surgical procedure removes vitreous gel (the clear fluid inside your eye) filled with blood or scar tissue, allowing light to reach the retina again. It helps restore vision and prevent retinal detachment.
5. Corticosteroid Treatment
Sometimes, steroid injections or implants are used to control inflammation and swelling in the retina. These are typically used when anti-VEGF treatments are not effective.
Preventing Diabetic Retinopathy
Although diabetic retinopathy can be managed, prevention is always better than cure. Here are some steps to protect your eyes:
- Maintain A1C below 7%
- Monitor your blood sugar daily
- Eat a balanced, low-sugar diet
- Exercise regularly (at least 30 minutes daily)
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
- Get a comprehensive eye exam once a year
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
To support eye health naturally, include these foods in your diet:
Diet Tips for Diabetic Eye Health
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale) – rich in antioxidants like lutein
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna) – omega-3 fatty acids protect retina
- Citrus fruits – vitamin C boosts eye tissue health
- Nuts and seeds – vitamin E fights oxidative damage
- Whole grains – regulate blood sugar levels
Avoid high-sugar foods, processed snacks, and trans fats.
When to See a Doctor
If you have diabetes, you should never skip eye check-ups. See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Blurry or fluctuating vision
- Floaters or dark spots
- Sudden loss of sight
Early intervention can make the difference between keeping and losing your vision.
Conclusion
Retinopathy treatment in diabetes focuses on controlling blood sugar, monitoring eye health, and applying timely medical treatments like laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, or surgery when needed.
With proper diabetes management, a healthy diet, and regular eye exams, you can prevent severe vision loss and protect your eyes for the long term.
Your eyes are precious — take care of them today to see a clearer tomorrow.
Leave a Reply