DEFINITION:
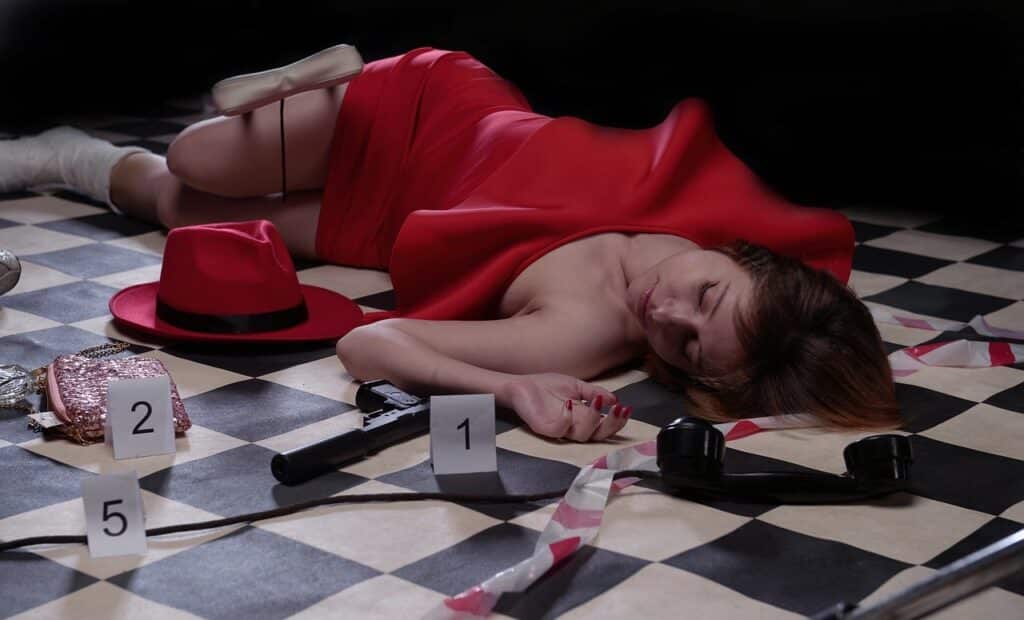

Trace evidence is material, the amount of which is small, but their importance is large in the detection of crime and criminals.
TYPES:
Trace evidence found at the Place of occurrence
Trace evidence was found with the corpse
Trace evidence found at the Place of occurrence
Fingerprint
Footprint
Hair
Blood
Fibres from clothes
Weapon
Poison vials
Seminal stains
Cigarette stump
Suicidal note
Trace evidence was found with the corpse
Hair
Blood
Fibres from clothes
Oil, grease, petroleum, and other similar substances.
Soil, mud, weeds, grass, etc
Saliva
Semen
Skin scrapping
Tooth/bitemark
Splinter, rope, string, etc
Bullet, gunpowder
MEDICOLEGAL IMPORTANCE
It is often a decisive factor in determining guilt
It often gives clues to an acquaintance
It often helps in the reconstruction of the occurrence of a crime
It often indicates the Place of occurrence
It often tells the time since the occurrence
It often locates criminals
SUPERIORITY
It is the actual evidence
Its presence is absolute proof of crime
Eye eyewitness may be false due to
Partisanship
Faulty memory
Defective observation
Only its interpretation may be wrong
LOCARD’S PRINCIPLE OF EXCHANGE
When two objects come into contact, there is always a transfer of materials from one to another.
So that traces from the scene may be carried away on the person or tools of the criminal, and at the same time, traces from all or any of these may be left at the scene or Place of occurrence.